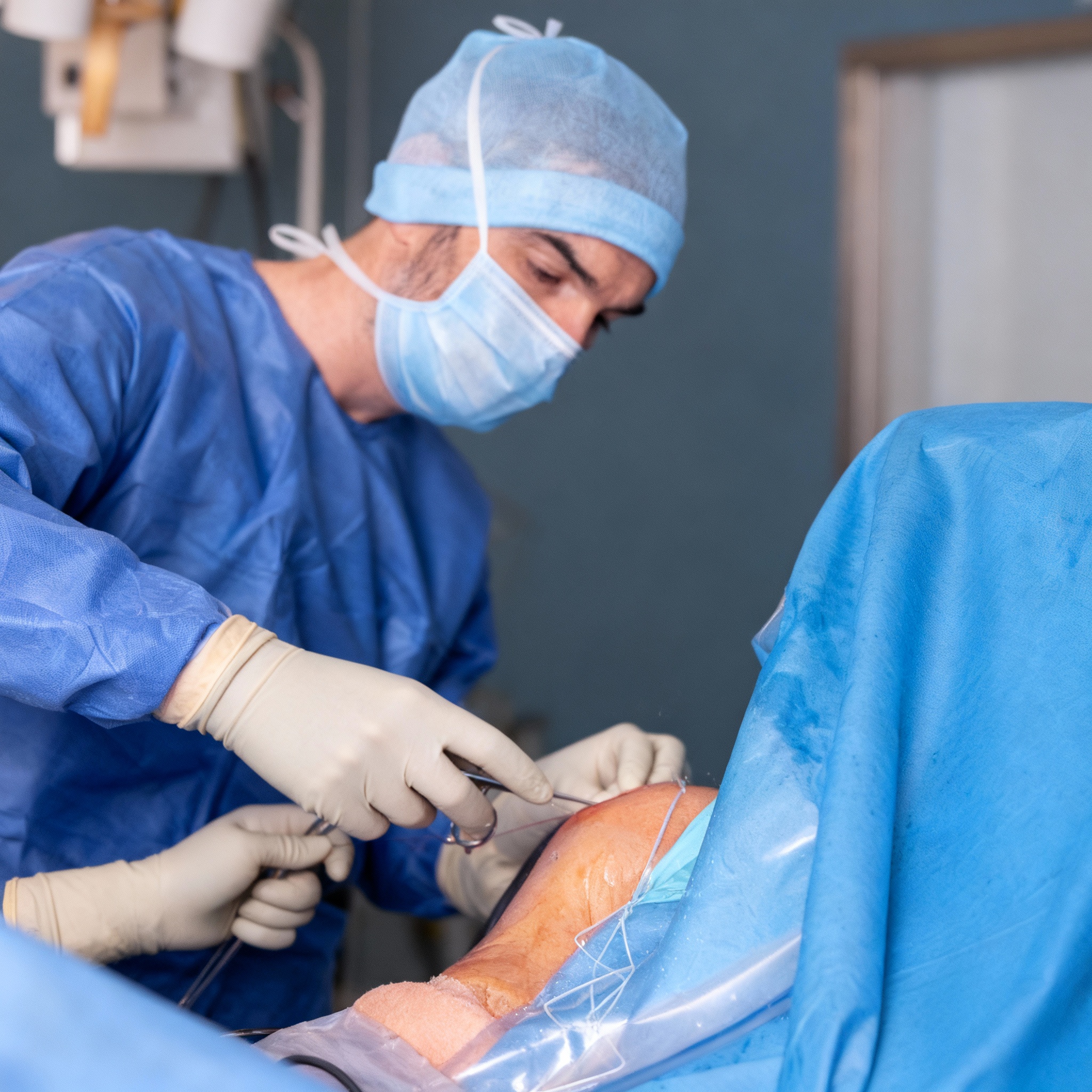
Fracture Osteosynthesis
Specialized management by Dr. Stéphane Vasseur
Indications
Osteosynthesis is indicated for displaced, unstable fractures or in patients with high functional expectations.
Surgical indications:
- Displaced fractures with pseudarthrosis risk
- Tuberosity involvement compromising function
- Associated skin or neurovascular lesions
- Patients with high functional expectations
Related pathology: Shoulder fractures
Operative principle
Reduction and internal fixation with plates/screws or nails according to the fracture pattern, under radiographic control.
The surgical intervention allows restoration of shoulder anatomy and function by fixing bone fragments in a stable manner to allow optimal consolidation.
Postoperative course and rehabilitation
- Immobilization varies 2–4 weeks depending on stability
- Early supervised mobilization, strengthening at 6–8 weeks
- Union 6–12 weeks
Risks
- Delayed/nonunion, stiffness
- Prominent hardware, infection (rare)
In practice
- Hospitalization: 1–3 days depending on fracture and stability
- Anesthesia: General ± regional
- Immobilization: 2–4 weeks depending on fixation stability
- Physiotherapy: Early mobilization then strengthening from 6–8 weeks